Coolant pumps | HELLA
General
Coolant pumps (Figure 1) are mostly driven mechanically, by a toothed belt or V-ribbed belt, and transport the coolant through the engine's coolant circuit. The pumps can be flanged directly to the engine or also installed away from it. The designs are quite different. Coolant pumps must withstand huge variations in temperature (-40 °C to approx. +120 °C). Changing speeds (500 - 8000 rpm) and pressures of up to 3 bar require high stability of bearings and seals.

Figure 1
Design/principle
A mechanical coolant pump consists of the following 5 sub-assemblies (drawing):
1. Body
2. Drive gear
3. Antifriction bearing
4. Mechanical seal
5. Vane
The drive gear and the vane sit on a common shaft. A mechanical seal seals off the pump shaft towards the outside. The rotation of the vane transports the coolant through the cooling system. Vanes are usually made of plastic or metal. The bearing load is lower with plastic vanes. At the same time, they are not as susceptible to cavitation.
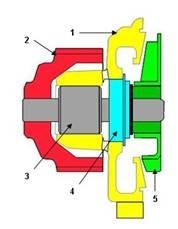
Drawing
Effects of a failure / causes
A failure of the coolant pump can manifest itself as follows:
- Noise
- Loss of coolant
- Inadequate cooling / engine overheats
These are possible causes:
- Mechanical damage:
Loose/broken vane
Bearing or seal broken
Drive gear damaged
- Cross-section constricted by corrosion or sealant
- Cavitation:
Damage to the vane by the forming and collapsing of vapour bubbles in the coolant (Figure 3)
- Electrical fault (short-circuit/interruption)

Figure 2

Figure 3
Possible damage patterns
Drive gear damaged (loose drive gear ring), Figure 4:
- tension of the control belt too high
- Misalignment of the belt
Fraction of the water pump bearing (bearing retainer):
- Heavy vibrations by defective Visco clutch

Bild 4
- Excessive application of sealant
Remains of the sealing compound (Fig. 5) may enter the cooling circuit and damage the mechanical seal, for example.

Bild 5
Corrosion in the entire cooling system (Figure 6):
- Defective cylinder head gasket - engine exhaust gases enter the cooling system. Negative variation of pH

Bild 6
Pump parts such as vane, body, mechanical seal and shaft severely damaged by hole corrosion (Figure 7):·
- Old/stale coolant with high content of chlorides (salt compounds) in conjunction with elevated temperatures.

Bild 7
Excessive leakage of coolant from the relief hole (Figure 8):
- Caused by corrosion in the cooling system

Figure 8
Notes on removal and installation
Always follow the instructions on the product leaflet and special installation instructions of the vehicle manufacturer when replacing the coolant pump. If the cooling system is contaminated, it must be flushed. The cooling system should only be filled with a coolant that meets the specifications of the vehicle manufacturer. The system must be filled or vented according to the instructions of the vehicle manufacturer. An incorrect installation can lead to overheating of the engine, damage to the belt drive or/and engine damage.