Reading the error memory
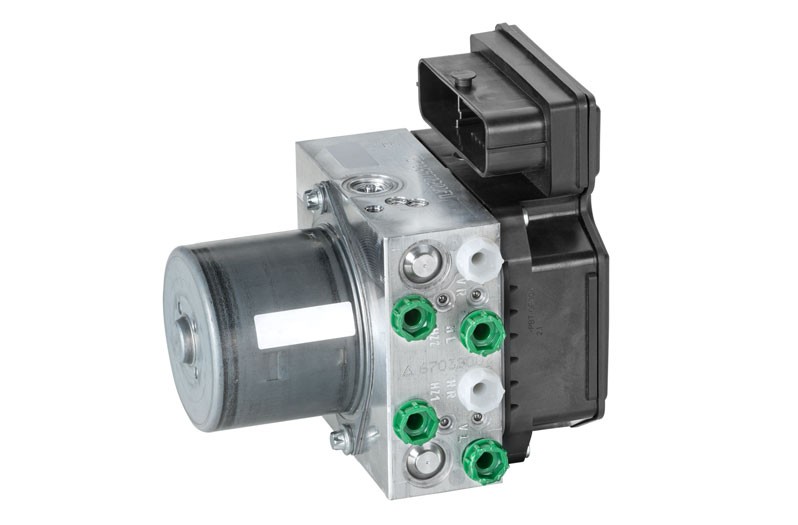
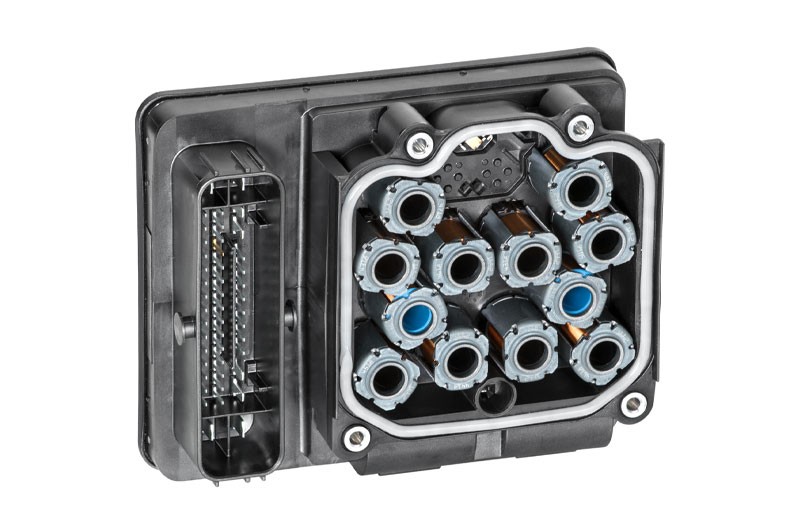
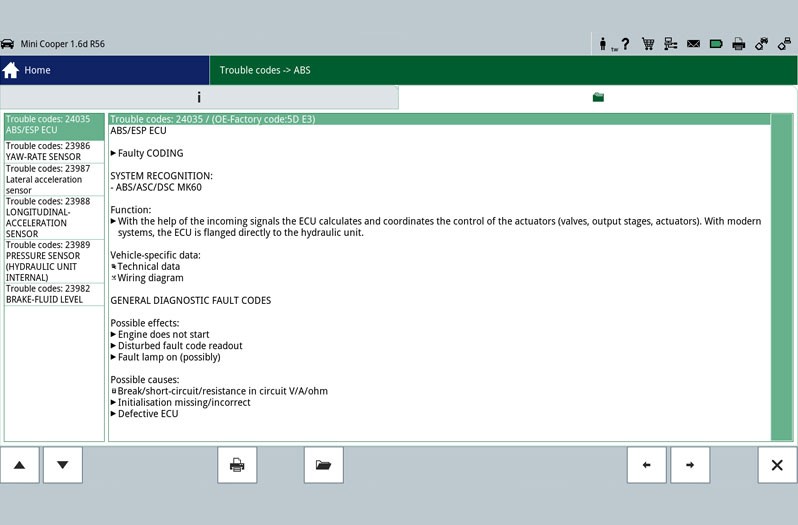
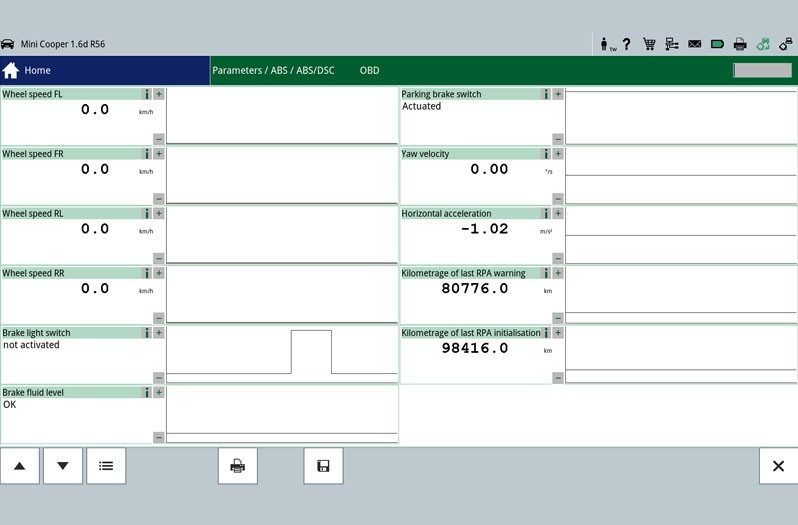
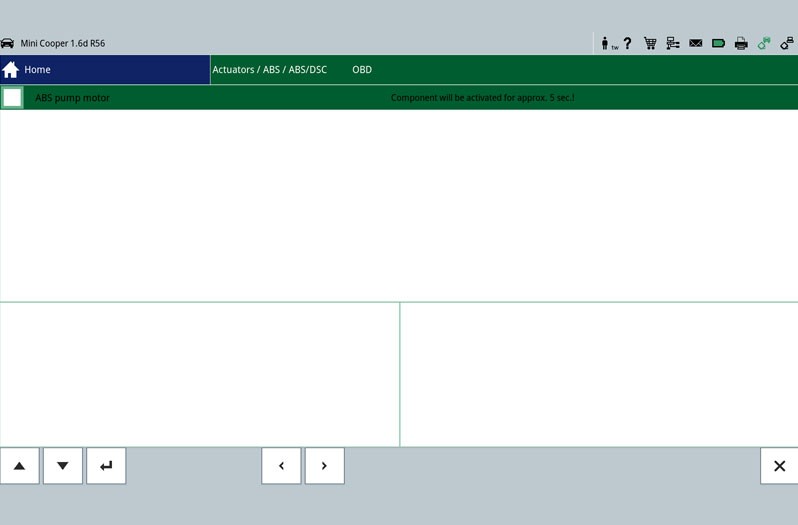
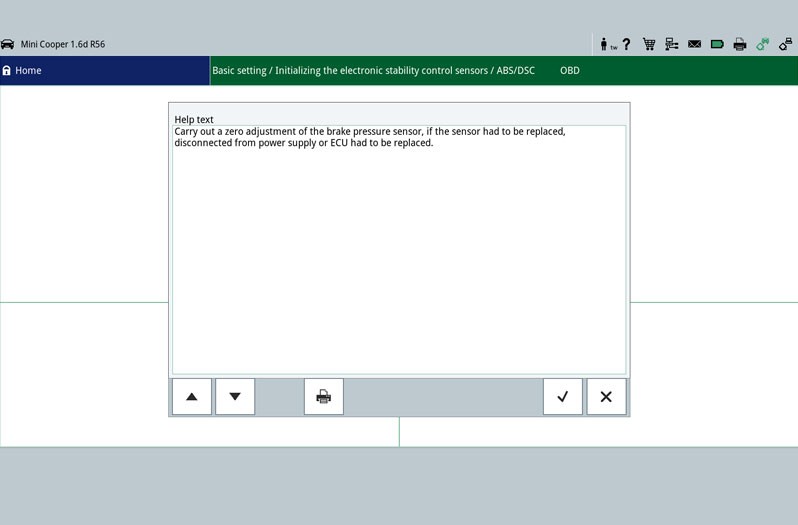
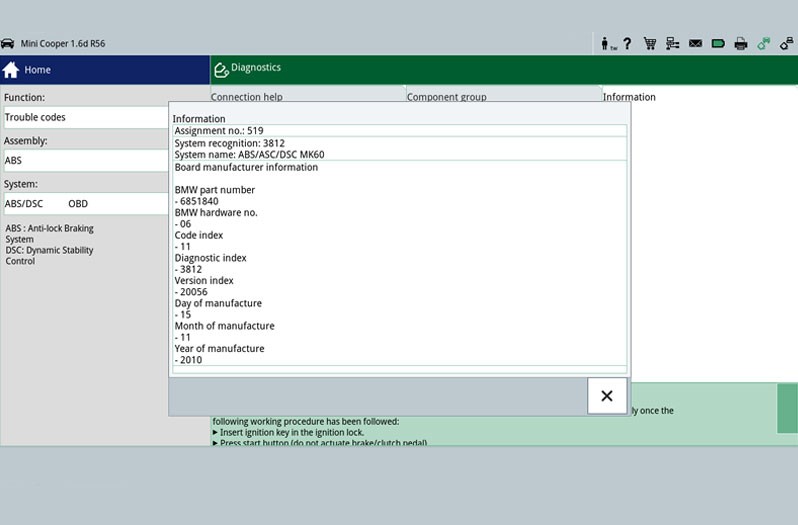
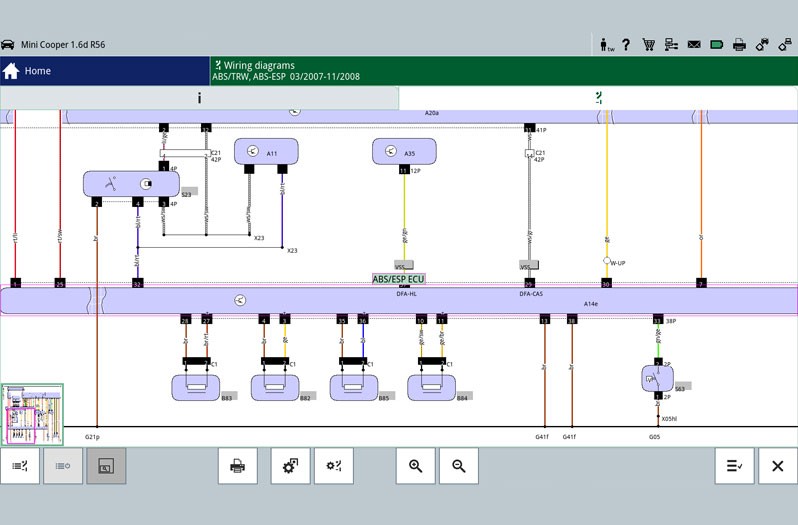
The first step is the reading out of the error memory. Any errors that occur are stored here and provide initial indications of the possible cause of the error. The stored error can give a direct indication about a defective component (Figure - Error memory 2) or about a short circuit/cable interruption. This allows targeted repair work to be carried out.