Tubos flexíveis dos travões e tubagens dos travões | HELLA
GeralOs tubos flexíveis dos travões e as tubagens dos travões do sistema de travagem hidráulico são utilizados como componentes de transmissão do líquido dos travões. As tubagens dos travões são, por exemplo, utilizadas para ligar o cilindro de travão principal aos componentes hidráulicos do travão de roda. Os tubos flexíveis dos travões são utilizados nas secções móveis entre a carroçaria e a suspensão, criando uma ligação flexível entre os vários componentes.A integração dos sistemas ABS, ESP e ASR nos veículos modernos implica um aumento substancial dos requisitos para estes componentes.Os principais requisitos são a resistência à pressão, resistência a cargas mecânicas e resistência térmica e química.RequisitosOs tubos flexíveis dos travões estão expostos às seguintes influências.Movimentos de amortecimento e de manobras da direção do veículoInfluências climatéricas, (calor, frio, ozono)Influências externas, (água, sal para degelar estradas, óleo)Impulsos de pressão hidráulicaDevido a esta panóplia de influências, os tubos flexíveis dos travões têm que ter excelentes características de resistência a impulsos, elementos de ligação robustos e uma longa vida útil.Estrutura do tubo flexível do travãoOs tubos flexíveis dos travões são compostos por uma borracha especial com malha integrada, a qual reforça substancialmente o tubo flexível e que serve de suporte de pressão.Revestimento interior do tuboPrimeira malha de reforçoCamada de cola especial com código de cor incorporadoSegunda malha de reforçoCapa do tubo flexívelCausas da avariaDefeitoFormação de bolhas na transição entre a válvula e o tubo flexívelCausaFugas no tubo flexívelMontagem defeituosa ou esforço mecânico excessivoDefeitoFormação de fissuras na capa do tubo flexívelCausaEnvelhecimentoMontagem defeituosa ou esforço mecânico excessivoDefeitoOxidação, tubos rígidos corroídosCausaEnvelhecimentoDanificação da camada isolante pelas influências ambientaisLocalização de errosOs tubos flexíveis dos travões e as tubagens dos travões são componentes de elevada relevância para a segurança e devem ser controlados durante todos os serviços de manutenção realizados ao veículo. Defeitos típicos são corrosão nas tubagens dos travões ou danos nas tubagens flexíveis. Estes defeitos podem dever-se a acidentes, a uma montagem incorreta ou ao envelhecimento dos materiais.Através de um controlo visual é, por norma, possível identificar facilmente pontos de fricção, fissuras, bolhas, corrosão ou outros danos externos.Aviso de montagemNo âmbito dos trabalho de reparação, o técnico deve prestar especial atenção aos seguintes avisosMontar os tubos flexíveis dos travões sem tensão e sem contacto com outros componentesEvitar torções dos tubos flexíveis, assim como pontos de fricçãoEvitar o contacto com óleo mineral e massas lubrificantesDeve ser assegurada uma distância mínima para evitar possíveis fricções e contactos durante movimentos dos amortecedores e manobras da direçãoEvitar a instalação nas imediações dos sistemas de gás de escapeEvitar raios de curvatura muito apertados (>40 mm)Aviso!Observar sempre os avisos de montagem dos fabricantes dos travões e do veículo.Uma montagem incorreta pode influenciar negativamente o comportamento de condução do veículo e colocar em perigo os ocupantes da viatura.
In hydraulic brake systems, brake hoses and brake lines are used to transfer brake fluid. Brake lines connect the actuation device, such as the brake master cylinder, to the hydraulic components of the wheel brake. Brake hoses are used as flexible connecting lines in all moving areas between the body and chassis.
With the integration of ABS-ESP and TCS systems in modern vehicles, the operative requirements placed on these components have risen dramatically.
Included among the main requirements are compressive strength, mechanical load-carrying capacity and thermal and chemical resistance.

Requirements
Brake hoses are subjected to the following influences:
- Vehicle steering and suspension movements
- Weather (heat, cold, ozone)
- External influences (water, road salt, oil)
- Pulses of hydraulic pressure
As a result of these influences, brake hoses need exceptional pulse strength, robust connecting elements and high fatigue strength.
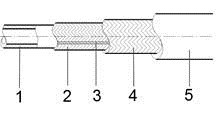
The structure of a brake hose
Brake hoses comprise a special rubber mixture and integrated braiding that considerably improves the strength of the hose and serves as a pressure support.
1. Inner tube
2. Initial reinforcement fabric
3. Special adhesive layer with embedded color code
4. Second reinforcement fabric
5. Hose cover
Causes of failure
Defect
- Bubbles forming where the tap and the braided hose join
Cause
- Leak in the hose sheathing
- Incorrect installation or mechanical overload

Defect
- Cracks forming in the hose cover
Cause
- Aging
- Incorrect installation or mechanical overload

Defect
- Oxidation, corroded lines
Cause
- Aging
- Insulating layer damaged due to environmental influences

Troubleshooting
Brake lines and brake hoses are safety-relevant components and should be checked every time the vehicle is maintained. Typical defects include corrosion on the brake lines and damage to the hose lines. These defects can be caused by accidents, improper assembly or aging.
By carrying out a visual inspection, it is usually possible to detect cracks, bubble formation, corrosion or other external damage with minimal outlay.
Assembly instructions
The following points should be taken into account by the technician when carrying out a repair:
- Mount brake hoses in a tension and contact-free manner
- Avoid twisting the hose and causing chafe marks
- Avoid contact with mineral oil and grease
- Ensure sufficient clearance for steering and suspension movements
- Avoid routing in the direct vicinity of exhaust systems
- Avoid excessively small bending radii (> 40 mm)
Note